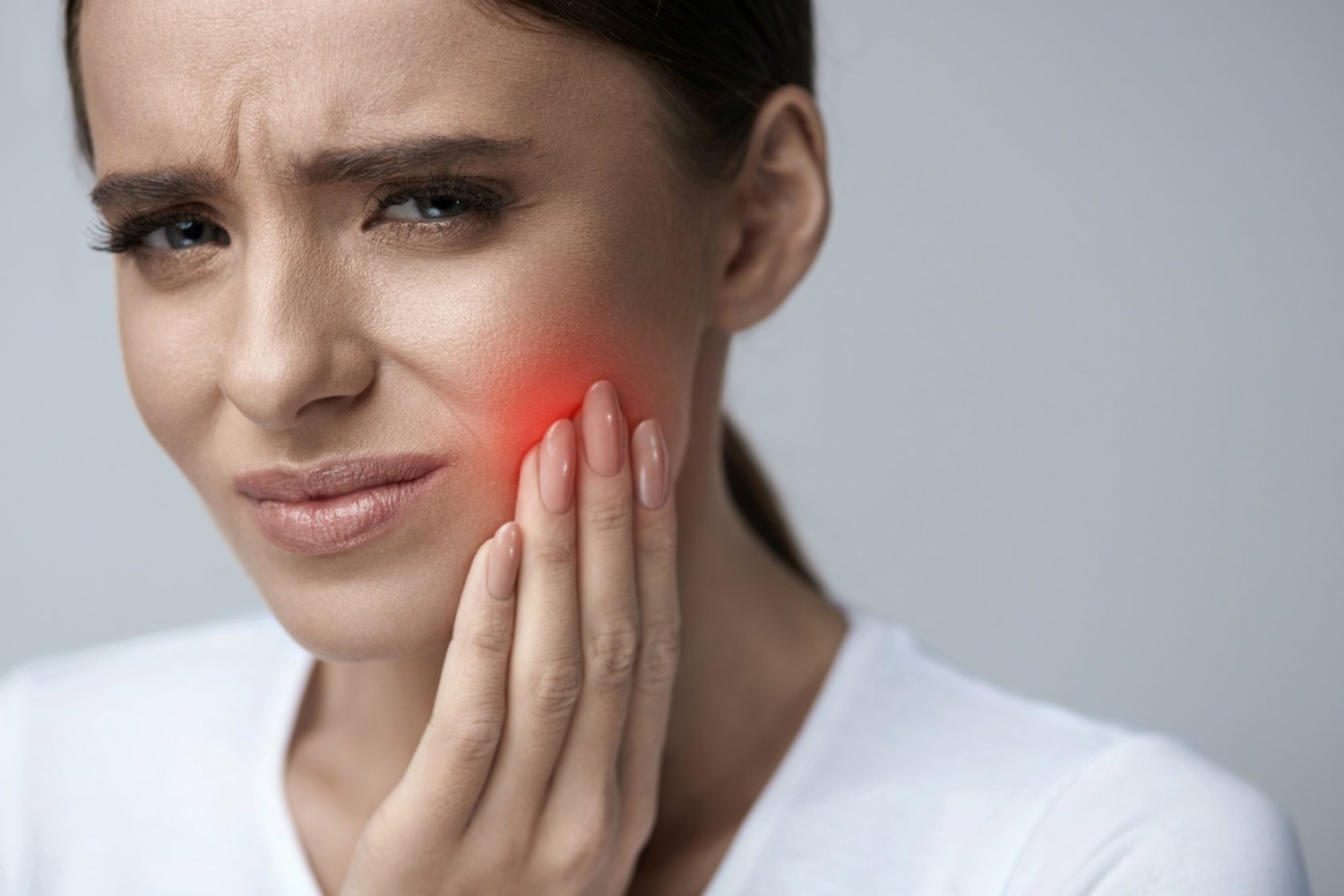
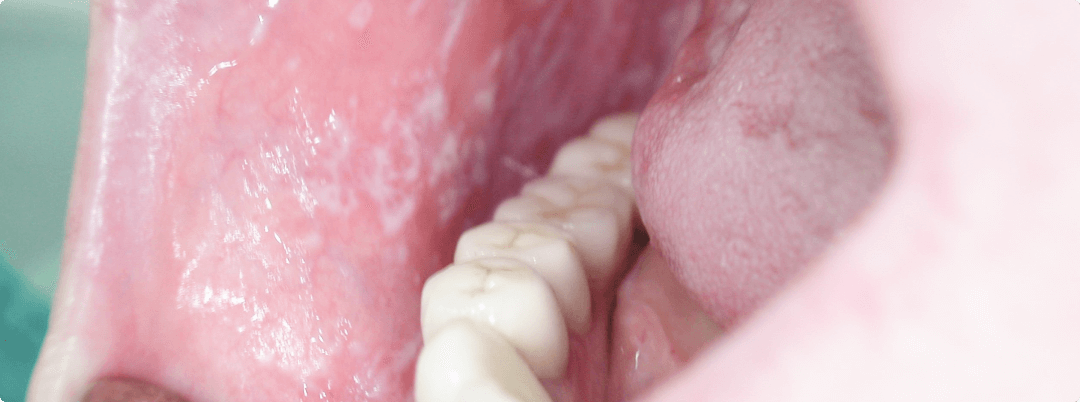
Stomatitis is the most common disease of the oral cavity. Both children and adults suffer from it. Its main symptom is ulcers, which can be different in shape and color. After their appearance in the mouth, there are always strong pain sensations. Why stomatitis occurs and how to avoid it — we will tell you in this article.
What is stomatitis?
Stomatitis is the name of a whole group of diseases that affect the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Almost every person on earth has encountered at least one type of stomatitis. The body does not develop immunity to it, and even on the contrary, the chance of getting sick with it again is high.
At the same time, some forms of the disease are very contagious.
There are no special tests for diagnosing stomatitis, so the doctor evaluates the degree of mucosal damage and the type of disease only with the help of an examination. At the same time, stomatitis itself can be a symptom of another, more serious disease, therefore, when diagnosing and drawing up a treatment plan, the overall clinical picture is important
Why can there be stomatitis
Experts still cannot say for sure why a person starts to get stomatitis. There are a number of possible reasons:
- damage to the mucous membrane, tongue and gums, for example, by dentures, fragments of teeth and overhanging edges of fillings
- allergic reaction to products, oral hygiene
- products concomitant diseases — for example, acute respiratory infections, herpes, diabetes
- poor oral care
- dental diseases (caries) and tartar
- general decrease in immunity, for example, due to frequent viral infectious diseases, vitamin deficiency or stress
- reduction of the protective properties of saliva
- violation of the microflora of the oral cavity and intestines
- poorly made, poorly installed or expired dentures
- microorganisms are pathogens that affect the oral mucosa
- systemic diseases of the body (anemia, metabolic disorders, hormonal and autoimmune problems)
- the use of certain medications
- bad habits (for example, smoking)
And, according to scientists, the cause of stomatitis may be toothpastes with sodium lauryl sulfate. Studies have shown that this substance provokes the development of chronic diseases of the oral mucosa, as well as their exacerbation.
Common symptoms of stomatitis
The symptoms of stomatitis depend on the form of the disease and on how badly the mucous membrane is affected. The main signs of stomatitis:
- Swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. This is the first sign of stomatitis. If you do not start treatment at this moment, then oval or round ulcers appear on the site of redness. They can be gray or white, with a red halo and a film on top.
- Pain in the area of foci of inflammation and ulcers. With severe stomatitis, ulcers literally sprinkle the inner surface of the cheeks and lips, and can also be under the tongue. As a rule, the pain is so strong that a person cannot eat.
- High fever and headaches. If stomatitis occurs in a mild form, that is, there are only 1-2 ulcers on the mucous membrane, then the temperature rises slightly. But when there are a lot of them, a fever begins, and the column on the thermometer creeps up.
When the first symptoms of any form of stomatitis appear, you need to seek help from a dentist. It is he who will identify the cause and prescribe the correct treatment. And the sooner you start it, the faster the symptoms of the disease will disappear.
Forms of stomatitis
- Catarrhal
This is the most common type of stomatitis. In this form of the disease, the patient complains of swelling and soreness of the mucous membrane. It turns red, may be covered with a white or yellow plaque, bleeding and bad breath appear. - Aphthous
It is characterized by the appearance on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity of aft — erosions of oval or rounded shape with a hyperemic (red) rim, covered with fibrinous plaque, soft, painful on palpation. Before the appearance of aphth, the mucosal area turns red and begins to protrude, a burning sensation appears. With a mild form of the disease, aft can be 1-2, and they heal on the fifth or sixth day. And with severe ulcers, there are much more ulcers, and after recovery, scars remain in their places. Such stomatitis has a chronic nature, and depending on the state of the body, the disease can manifest up to six times a year. - Candidal
The cause of the disease is the reproduction of fungi of the genus Candida, the number of which increases due to a decrease in immunity or prolonged use of antibacterial drugs. This form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of a white plaque on the tongue and oral cavity, a burning sensation, redness of the mucous membrane, an unpleasant taste in the mouth or loss of taste. Candidiasis stomatitis affects infants, as well as patients who use removable prostheses for a long time. - Herpetic (or herpes)
Both an adult and a child can get sick with it. There is such a form of stomatitis due to the herpes simplex virus, which, once in the body, remains in it forever. With this form of stomatitis, the mucous membrane first turns red. It becomes painful and sensitive to any external influences. Then the oral cavity is covered with small (3-5 mm) bubbles, which quickly break through, becoming round or oval ulcers — aphthae — with a narrow red rim and a white-gray plaque in the center. The process is accompanied by quite severe pain. Depending on the number of rashes, the disease occurs in mild, moderate or severe form, which is accompanied by a deterioration in general well-being and an increase in temperature, especially in children. - Allergic
In a child, it may occur as a reaction to a new product introduced into the diet. And adults may encounter this form of stomatitis due to weakened immunity or an inflammatory process in the oral cavity. The main distinguishing signs of allergic stomatitis are itching in the mouth, which increases after eating, the release of a large amount of thick saliva and very severe swelling.
As a rule, it is enough for a good dentist to examine the patient’s oral cavity and listen to his complaints to determine what form of stomatitis he has. The accuracy of the diagnosis is the key to the effectiveness of treatment.
How to treat stomatitis
Whatever the form of stomatitis, treatment always begins with a visit to the dentist.
He diagnoses and prescribes treatment. If necessary, you may need to consult other specialists, such as a gastroenterologist, immunologist or allergist.
Depending on the form of stomatitis, the doctor examines the patient and listens to complaints or prescribes laboratory tests, for example, bacterial culture of a smear or skin scraping, as well as a PCR study to determine the pathogen (herpes virus, fungus, etc.). Treatment of stomatitis usually occurs with the help of local remedies and includes:
- normalization and maintenance of high-quality oral hygiene
- spot treatment of ulcers with drugs with antimicrobial, antiviral or antifungal action
- pain relief with anesthetics
- reduction of puffiness and redness with anti-inflammatory drugs
In addition, part of the therapy is a special diet that will help reduce inflammation and will not irritate the mucous membrane.
What you can eat with stomatitis
Inflamed mucosa and ulcers in the oral cavity do not allow you to eat as usual. Therefore, during the illness, you have to change your eating habits. This is necessary to reduce discomfort, reduce inflammation and restore normal microflora. Warm food of a soft consistency that does not irritate the mucous membrane is recommended. With stomatitis, you can eat:
- warm fermented milk products (ryazhenka, kefir)
- compotes and jelly made from fresh berries or dried fruits
- liquid porridges
- meat and fish steamed and ground to a puree
- soups in lean broth
- cottage cheese dishes
If a child has stomatitis, then the diet depends on the age of the baby and on the form of the disease. More often, give the crumbs warm drinks that soften the mucous membrane and reduce the process of intoxication, especially after feeding. It can be a decoction of chamomile or even simple boiled water. And if an infant has stomatitis, then pay increased attention to the sterilization of bottles and nipples and breast treatment before and after feeding.
Regardless of the patient’s age, the stop list for patients with stomatitis includes:
- bread
- juices, berries and fruits
- smoked foods
- spicy and highly salty food
- chips and crackers
- fried fish and meat dishes
If you have stomatitis, then you will have to temporarily change your usual diet in favor of liquid or semi-liquid food. At the same time, you can not even eat soft bread or cookies, as they can injure the inflamed mucous membrane.
What will happen if stomatitis is not treated
- Chronic stomatitis
According to statistics, this is the most common complication.
It means that there will be a focus of infection in the body all the time. This means that the signs of the disease will periodically manifest. - The appearance of scars
Due to permanent non-healing ulcers, scars form on the mucous membrane - Laryngitis
If the infection passes to the respiratory tract, a cough appears, and the voice becomes hoarse. - Vision problems
With advanced herpetic stomatitis, the infection begins to affect the mucous membranes of other organs, such as the eyes. - Instability of teeth
Prolonged stomatitis will gradually lead to damage to periodontal tissues and as a result may cause loosening of teeth
How not to get stomatitis again
After the acute period of the disease passes, discomfort and bleeding disappear, it is recommended to undergo professional oral hygiene. It is conducted by a hygienist. With the help of ultrasound, he will remove tartar and soft plaque, and with them dangerous microorganisms. In addition, it is necessary to cure teeth affected by caries, to correct or replace orthopedic structures and prostheses. All this will help to avoid relapse.