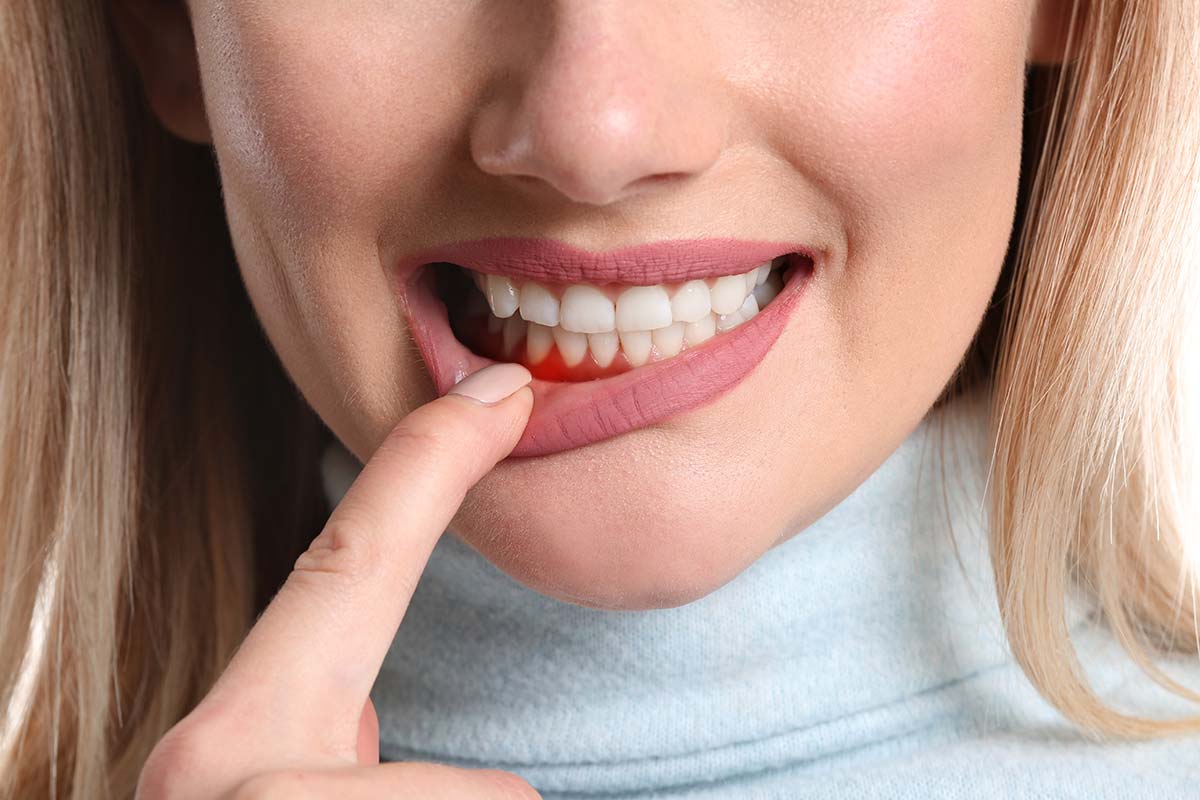
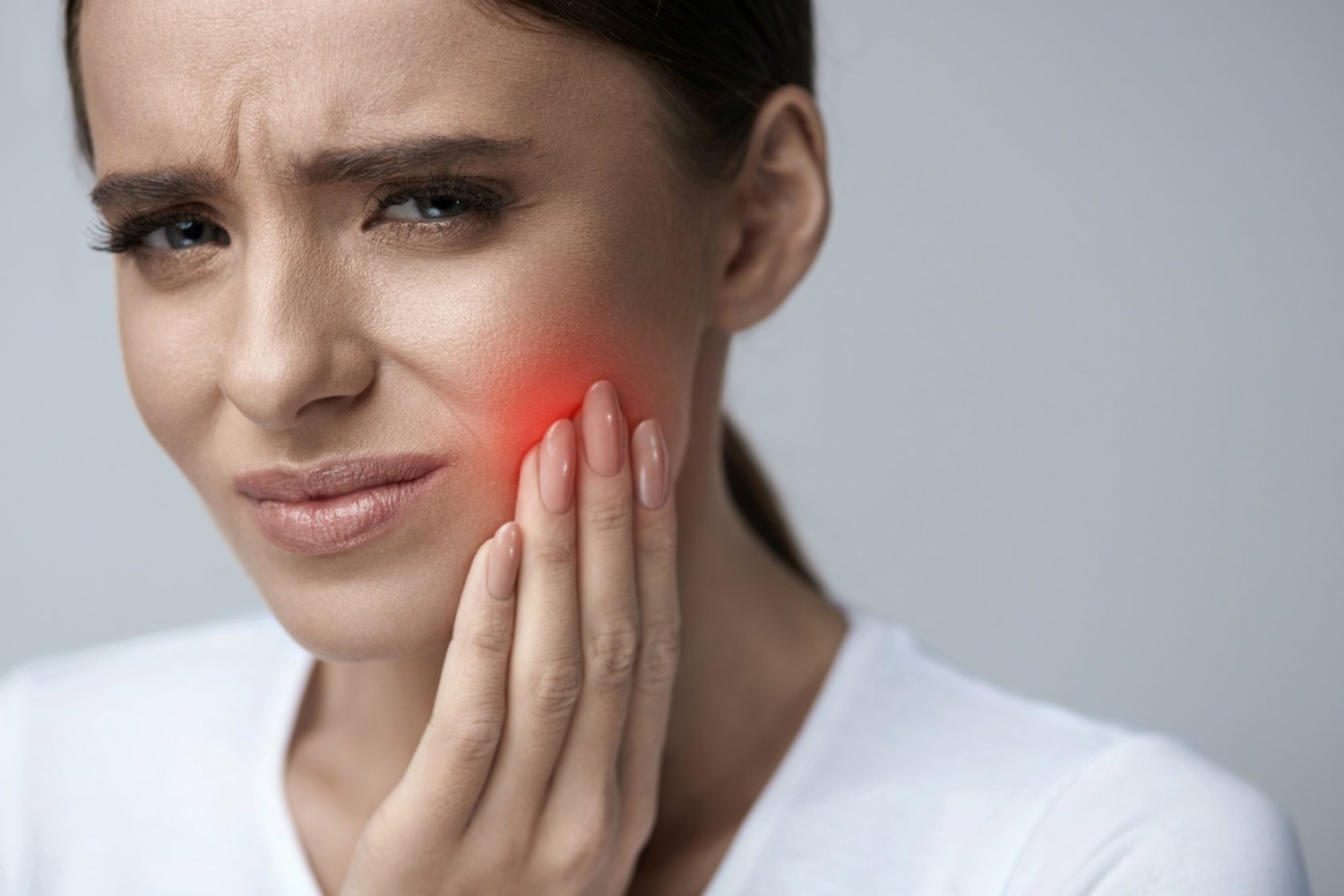
According to statistics, about 95% of the country’s residents suffer from periodontal diseases. The reasons for this are a low level of home hygiene, unwillingness to resort to professional medical care in the early stages of gum disease and to undergo timely preventive examinations.
Self-treatment is especially popular: without a doctor’s prescription, herbal gargles are actively used, special toothpastes are bought, ointments and antiseptics are rubbed in. As a consequence – such high rates of morbidity. At the same time, of all gum diseases, 3% of all gum diseases fall on the insidious periodontal disease. What is the danger of periodontal disease, what causes it and whether it can be cured – we answer the most worrying questions.
Periodontal disease – what is this disease
Periodontal disease is a systemic lesion of periodontal tissues, arising due to metabolic disorders and blood supply in the gums. To date, periodontal disease is incurable and is characterized by an unfavorable prognosis for the patient, namely the complete loss of teeth. The disease does not occur in one day – it develops asymptomatically over several years. The appearance of the first symptoms indicates the presence of exacerbation and progressive development of the pathological condition.
Scientists have established: if there are clear symptoms of periodontal disease, it means that the disease runs for at least 15 years.
Periodontal disease or periodontitis?
Many patients confuse these two diseases. And this is not surprising: in the past, all diseases of the gums were called periodontosis, so this word still prevails in the popular lexicon. Now this term is outdated, and in medicine instead of it “periodontitis” is used. However, the disease “periodontosis” is real, although it is quite rare, which can not be said about periodontitis.
Periodontitis and periodontal disease are two completely different diseases, differing in their symptomatology and course. If in the case of periodontitis the main symptoms are inflammation of periodontal tissues, bleeding gums and mobility of teeth, in the case of periodontal disease – the destruction of the supporting apparatus of the tooth without signs of inflammation, soreness and bleeding. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.

Causes of periodontal disease
The causes of the disease are not fully understood, but its development is often influenced by systematic diseases of a general nature, such as:
- genetic predisposition
- improper bite
- endocrine disorders
- diseases of the cardiovascular system
- gastrointestinal diseases
- arterial hypertension
- hypovitaminosis
In the zone of special risk are smokers, pregnant women, as well as people who neglect regular oral hygiene and their health in general. The saddest thing is that periodontal disease develops at any age, including in children.
Symptoms of periodontal disease
The symptomatology depends on the severity of the disease. But here, too, not everything is so simple. It is impossible to detect periodontal disease on your own at the initial stage: the disease is practically asymptomatic and painless up to the severe stage.
The following signs should alert you and make you see a dentist immediately:
- pallor and thickening of the gums
- discomfort and itching in the gums
- non-carious lesions and enamel discoloration
- tooth elongation and thinning
- tooth root exposure
Usually, patients first come to the doctor with a complaint of increased tooth sensitivity, and after radiologic examination an accurate diagnosis is made.

Stages of periodontal disease
Despite the lack of a unified view of doctors on the origin of the main types of this disease, there are currently about a hundred different classifications of periodontal disease. We will cite the most common of them – according to the severity of the disease.
There are three main stages of periodontal disease
- Mild degree
The patient begins to be bothered by a slight sensitivity of the teeth at temperature changes. Initial signs of bone atrophy appear, which are visible only on radiologic images. - Middle degree
The gingiva settles, the roots of the teeth are exposed, significant tooth gaps appear. Wedge-shaped defects are possible. The doctor determines the destruction of bone tissue more than a third of the length of the root. - Severe degree
The roots of the teeth are exposed for more than half of their length. The teeth are very sensitive. The bite is deformed. There is significant tooth mobility and then tooth loss.
Treatment
You will ask: “How to treat periodontal disease, if this disease belongs to incurable?”. That’s right: this disease can not be cured, but you can achieve a remission stage. If we talk about the treatment of periodontal disease at home, it is definitely contraindicated – no folk remedies will not help here. Only a periodontist with the help of modern therapeutic methods is able to slow down the process of bone atrophy and suspend the development of complications. From the patient will require patience (treatment will be long) and compliance with all medical recommendations.
Treatment of periodontal disease is carried out comprehensively and is aimed at relieving the main symptoms, improving blood supply to the gums, restoring the aesthetics and functionality of the teeth.
- Therapeutic treatment
consists of professional hygiene and sanitation of the oral cavity. The presence of carious lesions and tartar only aggravates the situation. - Physiotherapeutic treatment
Massage, electrophoresis, ultrasound therapy, baths, rinses improve the condition of the gums, reduce the sensitivity of the mucosa. - Drug treatment
Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, immunostimulating, hormonal drugs, as well as multivitamins are prescribed. - Injection therapy
Plasma therapy helps to improve blood circulation and slow down the processes of atrophy. - Dental splinting
is indicated in case of pathological mobility of the teeth to strengthen them. The type of splinting structure is selected individually. - Surgical treatment
is performed in case of severe bone atrophy in order to restore bone tissue and prevent premature loss of teeth.
In addition to dentists, the patient must necessarily undergo a comprehensive diagnosis with other specialized specialists to identify and eliminate the underlying cause of periodontal disease.
Complications
The main complication of periodontal disease is premature loss of bone tissue and teeth, as well as the associated negative consequences. The absence of teeth leads to a significant reduction in the quality of life and various psychological problems in the patient.
In addition, scientists have proven that people with periodontal disease die earlier and are susceptible to the development of cancer. Therefore, this diagnosis, although rare, requires urgent comprehensive treatment by qualified specialists.